Portfolio management is concerned with the act of selecting the appropriate combination of investible instruments and policies in the right proportion. It consists of matching investment to goals, allocation of assets for individuals and institutions to generate optimum returns while stabilizing the investment risk against investment performance. Portfolio management is one of the most significant skills required for the management of investment effectively. It is the management of the range of financial stocks securities such as bonds, shares, cash, and mutual funds to achieve maximum profits from the investments within a time period, usually one financial year. Often students seek Portfolio Management Case Study Assignment Help to write an effective case study.
Professional experts at MyCaseStudyHelp.Com are able and dexterous to deal with any query regarding the academic assignment. They have adequate ideas and knowledge about the pros and cons of various securities options for making an investment. You get a one-stop solution on our website. We are one of the most preferred Assignment Help providers in Australia. You can make your Case Study On Portfolio management perfectly by getting our help.
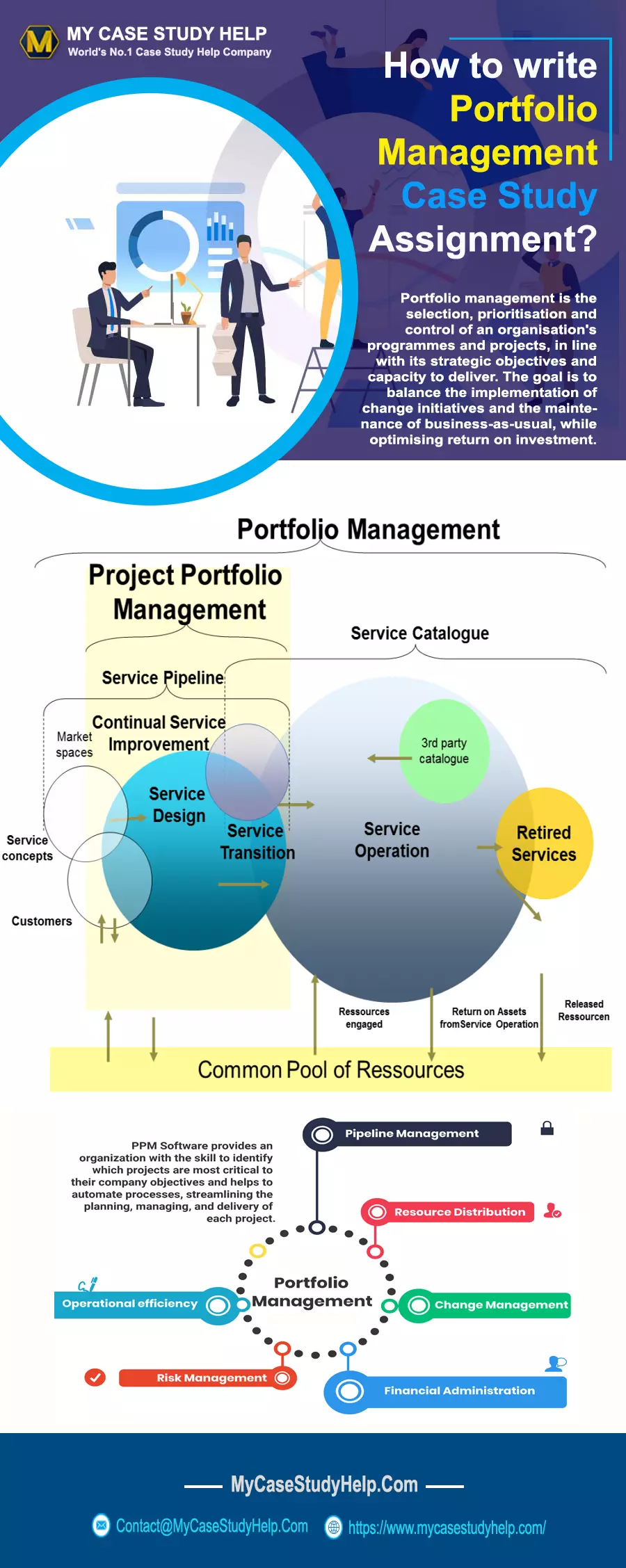
Understanding the term portfolio management
Portfolio management is termed as the act of deciding about financial investment mix and policy and asset allocation. It is the course associated with managing a range of financial stock securities. It starts with describing the investment strategy for the investor. Then it determines the investor budget and resources within the ambit of which the investment requires. Further, it is essential to figure out the expectations or required returns and investor’s risk intensity that is possible when investing. Moreover, the manager starts allocating the resources to the investor and invests in a proper blend of resources, including fixed income securities, real state, equity, mutual funds, derivatives, and bullion.
The manager is then required to determine and allot the investment inside the asset class, such as stock in the sector and sector inequities. Further, the manager tries to balance the portfolio to complete the risk and return objective. The manager determines the portfolio performance and assesses whether the portfolio meets the stated goals. In the next step, they review the performance make appropriate modifications to maintain the goals. Investors want to handle their investment or assets to receive maximum value or maximum utilization in the long term.
The key elements of portfolio management
Asset allocation: Asset allocation follows the concept that different assets do not move identically, and some of them are unpredictable than others. Efficient portfolio management must have a long-term mix of assets. Its motto is to have an optimum risk or return profile of an investor that is done by investing in an asset mix with low correlation.
Diversification: The primary approach in investment is to make a collection of securities that give a huge impact within the class of an asset as the determination of winners and losers in a consistent manner is not possible. The division of risk and reward within the category of an asset is termed diversification. It helps the capturing of potential returns of all the subsets of an asset class.
Rebalancing: It is a technique used to align the returns of a portfolio to the objective for which was initially determined for it at a regular period. It refers to adjusting the weightings of an asset portfolio. It involves buying or selling stocks, funds, or securities periodically to maintain the desired level of asset allocation. Rebalancing twice a year is enough as it ensures that asset allocation is not getting out of the command.
Types of Portfolio management
- Active Portfolio Management: In this portfolio management, project managers are actively involved in buying and selling securities to earn maximum returns. They aim to ensure better returns compared to what the market dictates.
- Passive portfolio management: It is the opposite of active portfolio management. Portfolio managers follow a fixed portfolio that is aligned as per the present market trends.
- Discretionary Portfolio Management: In this portfolio management, the managers have complete freedom to make decisions on behalf of the investor. They adopt a suitable strategy after considering individuals’ goals and time frames.
- Non-Discretionary Portfolio Management: The non-discretionary portfolio manager advises the investor concerning the routes which are best to take. They clearly outline the pros and cons, and it is the choice of the investor whether he accepts or rejects their suggestions.
Objectives of portfolio management
- Portfolio management meets the tailored and customized investment needs of the investors.
- It works on the principle of risk reduction through diversification.
- It provides investment alternatives to people according to their income, budget, time frame, and risk tolerance.
- Portfolio management schemes support both tax planning and tax saving.
- Diversification of funds facilitates both capital appreciation and safeguard of the principal amount invested.
- It offers liquidity, marketability, diversification, and consistent returns.