An accounting information system is a technique that a business organization uses to gather, store, process, manage, retrieve, and report its financial data. It can be used by a business analyst, accountant, consultants, managers, chief financial officers, regulators, auditors, and tax agencies. Digital technology has revolutionized the way of accounting. Advances in information technology indicate that most manual accounting system has been replaced by accounting information system that is faster and more accurate than that. Accounting information is required by managers to establish and achieve organizations’ future strategic goals. University students feel trouble when they have to write a case study on it as they do not have sufficient knowledge about the concept and techniques of accounting information systems.
There is always a question in students’ minds; How To Write An Accounting Information System Case Study efficiently? We at MyCaseStudyHelp.Com enable students to make their case study perfectly by providing complete assistance on it. We are associated with several experts to guide you on the techniques of making an impactful accounting information system case study.
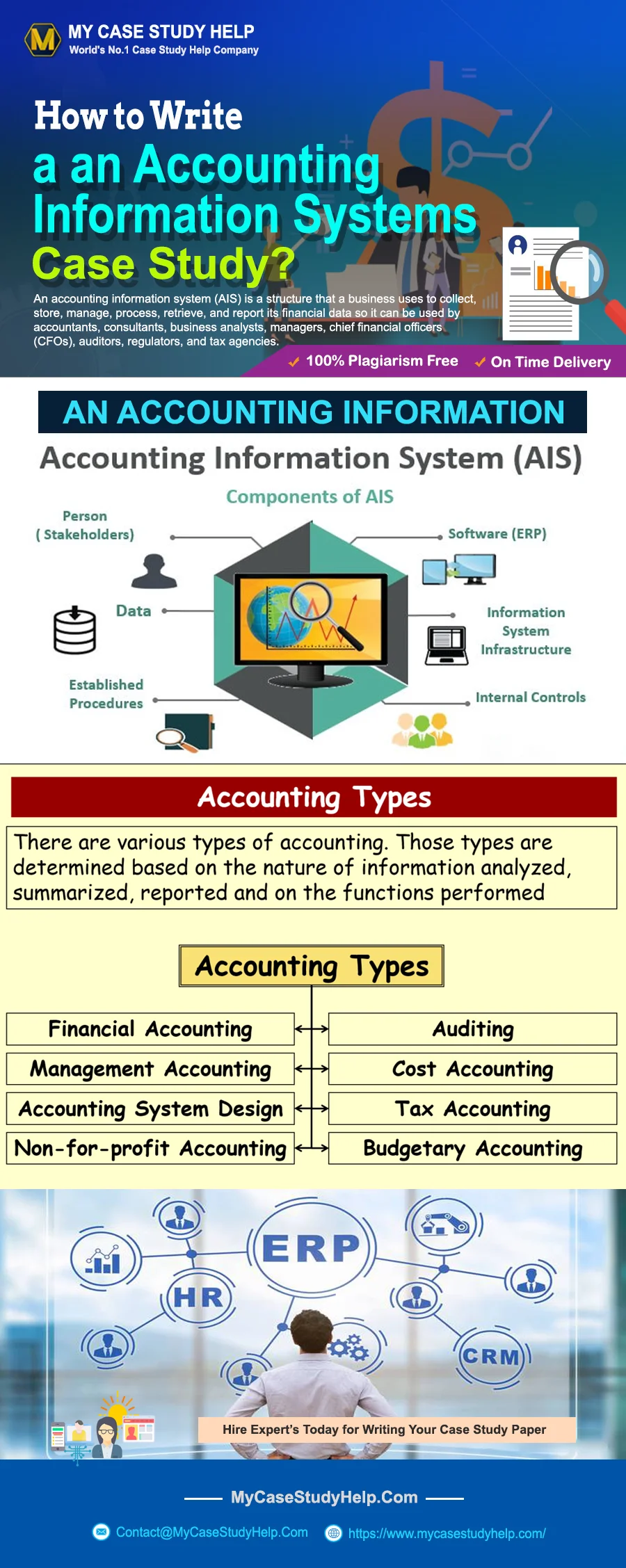
Overview of accounting information system
An accounting information system is a process of handling all accounting and business activities for a business organization. An accounting system is concerned with the set of human and capital resources within an organization that is liable for gathering and processing data to produce useful information to the entire management level in planning and controlling the organization’s activities. To attain decision-making success, accounting should be of high-quality relevant and useful in the decision-making process. An accounting information system usually comprises six primary elements: people, procedures and instructions, information technology infrastructure, data, software, and internal controls.
Case Study Accounting Information System
Accounting information system people: The people in an accounting information system are the system users. AIS help different departments in a company to work together. Different professionals may use AIS such as accountants, business analysts, managers, auditors, chief financial officers, and consultants. The AIS should be designed to cater to the need of the people who use it.
Procedure and instructions: The procedure and instructions of AIS are the techniques of collecting, retrieving, storing, and processing data. These techniques are both manual and automated. The data come from both internal sources as well as external sources. The procedure and instruction can be coded into the AIS software. However, the procedure and instruction can also be coded into employees via training and documentation.
Accounting Information System (AIS) Data: An AIS need to have a database structure to collect and store information like a structured query language. The AIS need various input screen for the several types of system users and data entry as well as several output formats to fulfil the needs of different users and several types of information.
Explain 10 ways in which an accounting information system can add value to an organization
AIS Software: The software element of AIS data is the computer program used for storing, processing, retrieving, and analyzing the financial data of a firm. Today almost all companies use computers software as the basis of the AIS instead of the manual paper-based system. AIS software programs should be customized to fulfill the unique needs of the different types of businesses.
IT infrastructure: Information technology infrastructure is a name for the hardware used to operate the accounting information system. Hardware items a business needs to have are computers, servers, printers, routers, mobile devices, storage media, and a backup power supply. The hardware chosen for AIS should be compatible with the intended software.
Internal controls: The internal controls of an IAS refer to the security measures that protect sensitive data. It is simple as a password and complex as biometric identification. Biometric security protocols store human characteristics that don’t change with time like fingerprints, iris scanners, facial reorganization, and voice. AIS must have internal controls in order to protect against unauthorized computer access and to limit access to authorized users.